YouthThrive
Across the country, parents, programs, organizations and local, state and federal agencies have embraced a new approach to helping families thrive AND promoting children’s best development.
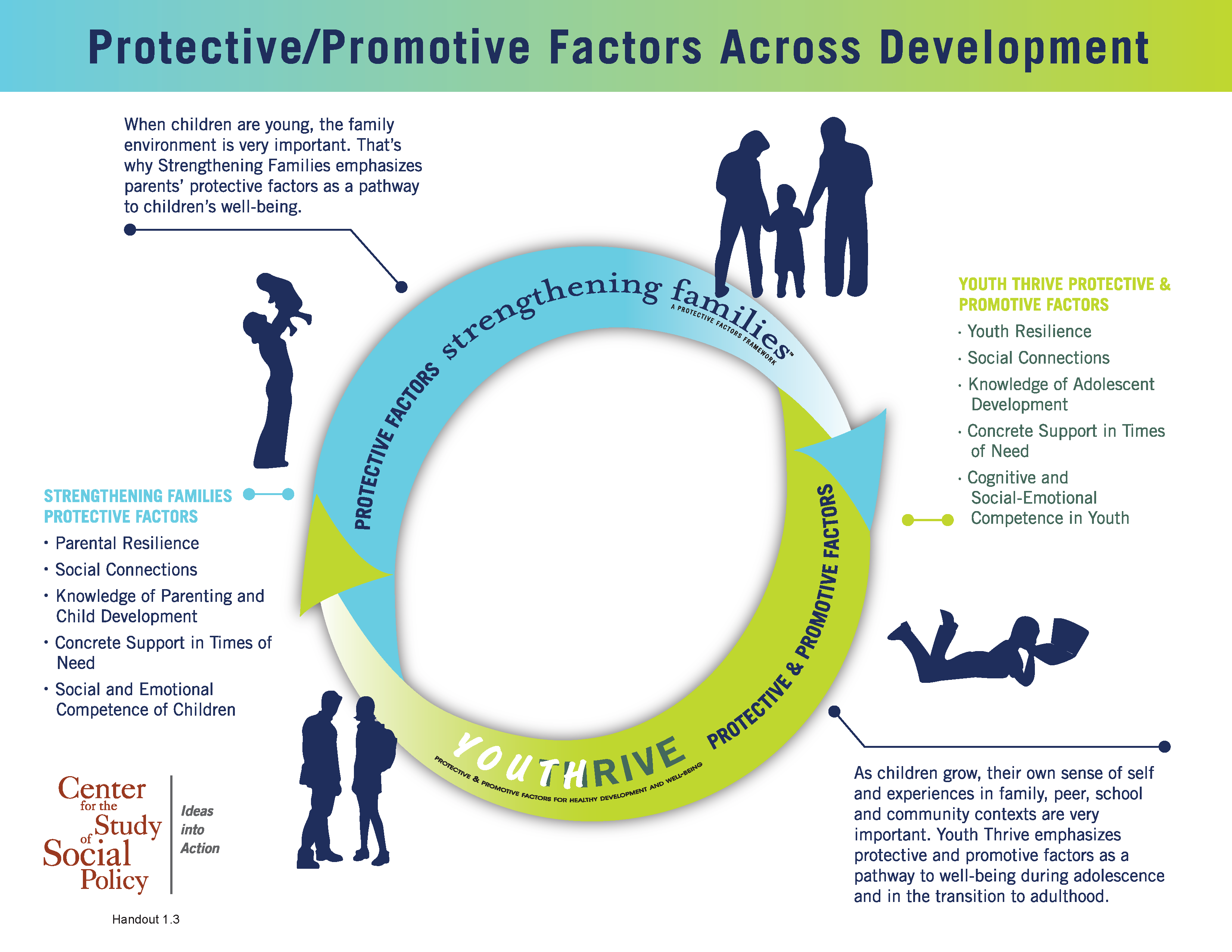
YouthThrive Protective and Promotive Factors
Factors that both mitigate risk and enhance healthy development and well-being for youth.
Youth Resilience: Internal, adaptive traits that evolve from youths’ positive or adverse life experiences, and that enable youth to survive and thrive:
- positive identity, positive self-concept
- self-worth
- self-compassion
- sense of competence and self-efficacy
- sense of personal responsibility
- autonomy
- timely help-seeking
- belief in one’s ability to influence the environment positively
- self-advocacy
- healthy coping
Social Connections
- Physically and emotionally safe, stable and supportive environments including equitable schools, communities and social institutions
- Healthy, supportive, caring relationships with family and other adults who provide positive advice; promote high expectations; and set developmentally appropriate limits, rules and monitoring
- Healthy, supportive, caring relationships with peers and intimate partners
- Opportunities for constructive engagement in family, school, community and social institutions
Knowledge of Adolescent Development
- Youth and adults have accurate information about youth biopsychosocial and cognitive development, including the impact of trauma
- Youth and adults have accurate information about preventing negative outcomes for youth (e.g., substance abuse, pregnancy, suicide, gang involvement)
- Youth and adults recognize that all youth have strengths and capacities
Concrete Support in Times of Need
- Opportunities for additional skill building (e.g., tutoring, counseling)
- Crisis assistance (e.g., mental health, substance abuse, intimate partner violence, health, housing, workforce development, legal, recreation, respite)
- Psychoeducational assistance (e.g., cognitive, behavioral and academic assessment and services)
Cognitive and Social-Emotional Competence: Youth engage in behaviors that promote healthy biopsychosocial and cognitive development, including:
- Exercising self-regulation and impulse control
- Building critical thinking, planning, decision-making, conflict-resolution and communication skills
- Displaying a sense of right and wrong
- Understanding one’s personal developmental history and needs
- Committing to realistic, productive goals, positive work habits, activities, values and beliefs
- Experiencing positive emotions (e.g., joy, love, hope, optimism, trust, faith)
- Demonstrating character strengths (e.g., respect, compassion, integrity)
- Identifying productive interests and seeking to excel
- Forming and sustaining healthy relationships
- Engaging in positive risk-taking
- Avoiding drugs, alcohol and risky sexual activity
- Building essential life skills (e.g., financial management, self-care, home maintenance)
- Deepening cultural knowledge
- Exploring spirituality
- Consuming nutritious foods and exercising within one’s physical means
Learn more about YouthThrive at the website of the Center for Study of Social Policy.





